The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires the use of the “constant yield method” to amortize bond premiums or discounts. This applies when the bond's purchase price differs from its face value. TValue software is an excellent tool for performing this calculation.
When you purchase a bond, you typically pay the market price, which may be more or less than the bond’s face value. Upon maturity, you will receive the bond’s face value. Any premium paid above the face value results in a loss, while a discount creates a gain. The constant yield method spreads this gain or loss over the bond's life by amortizing the premium (as an expense) or discount (as income) each year.
The constant yield method is a technique used to amortize the premium or discount on a bond over its life. To apply this method, you first need to determine the bond’s cash flows. Below, we have a bond for $100,000 with a 4% semiannual coupon for 5 years.
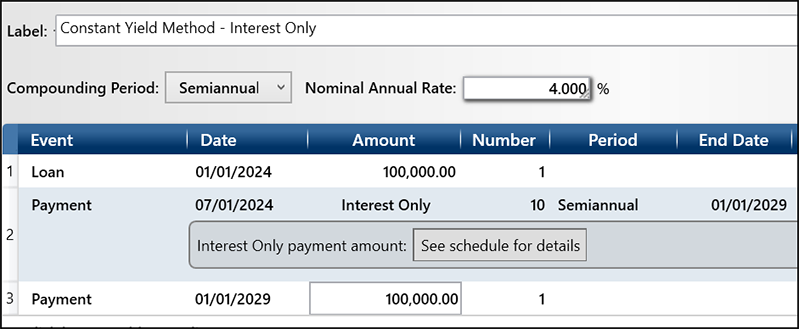
On the amortization schedule, you will have your cash flows (Interest Only Payment) to amortize the premium or discount.
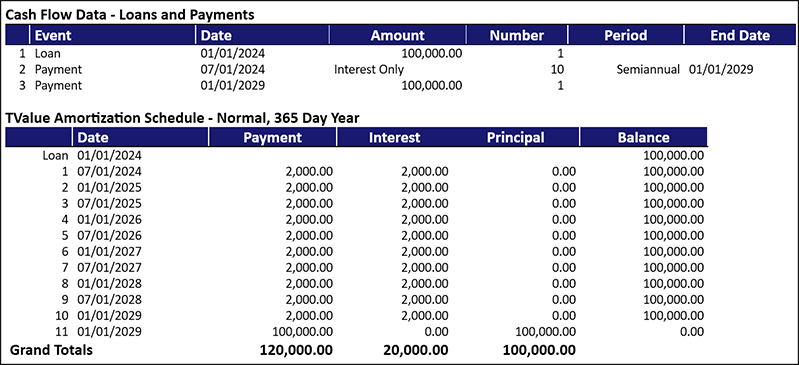
The next step is to determine your yield to maturity or the discount rate that equates the present value of the bond to the price you paid. You can determine the yield from the following variables: price paid, cash flow (payments), years to maturity, and bond’s value at maturity. Once you solve for the yield, your amortization schedule will show the accretion amount for each period.
In this example, open a new schedule with Semiannual compounding and enter the price paid for the bond of $98,000. On line 2, the Payment is $2,000 for 10 semiannual periods. On line 3, enter the maturity date and the amount of the bond. Then type “U” for the Nominal Annual Rate and click Calculate. The result is the actual yield of the bond is 4.451%.
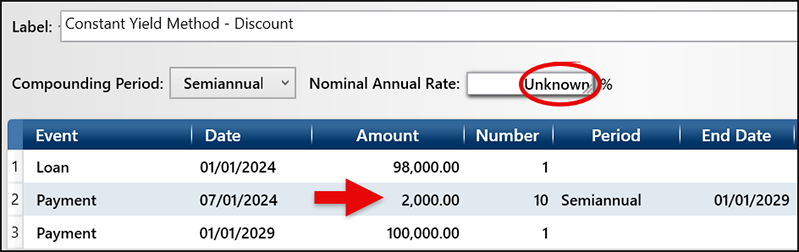
The amortization schedule will show the amortized premium or discount from the “Principal” column.
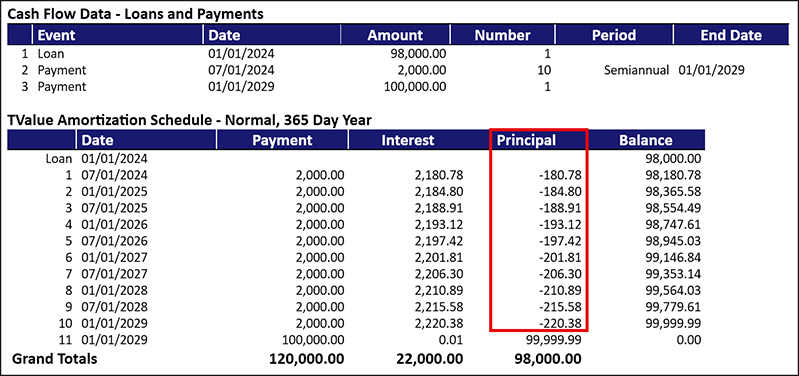
This can be a fairly simple calculation. However, if there are principal payments during the term, the calculation becomes more complicated and requires additional steps to do the amortization.
If you need any help with these calculations, please give TimeValue Software Support Team a call at 800-426-4741 or you can email support@TimeValue.com.